The limitations of financial statements include their historical nature and the use of estimates. Financial statements may not reflect current market conditions and can be affected by management bias.
Financial statements are important tools for stakeholders to assess the financial health of a company. However, they have certain limitations that can impact the accuracy of the information they provide. Understanding these limitations is crucial for making informed decisions regarding investments and business operations.
We will explore the constraints of financial statements and their implications for stakeholders. By gaining a clear understanding of these limitations, individuals can better interpret financial data and make more informed decisions.

Credit: www.studypool.com
Challenges In Accuracy
Ensuring the accuracy of financial statements is of utmost importance for businesses and investors. However, there are several challenges that can hinder the accuracy of these statements. This section will discuss two common limitations – errors in data entry and dependence on estimates – and their implications for financial reporting.
Errors In Data Entry
Data entry errors are a significant challenge in maintaining the accuracy of financial statements. Mistakes can occur during the recording and inputting of data, leading to incorrect figures and compromising the integrity of the statements.
These errors can arise from a variety of sources. They may result from a simple typographical mistake, where numbers or labels are entered incorrectly. Alternatively, errors can stem from inconsistencies in the recording process, such as double-entry errors or misplaced decimal points.
The impact of data entry errors can be far-reaching. Inaccurate financial statements can misrepresent a company’s financial position, profitability, and cash flows. This can ultimately misguide investors and stakeholders, affecting their decision-making process and potentially leading to negative consequences for the business.
Dependence On Estimates
Financial statements often rely on estimates, especially in areas where precise figures are difficult to determine. These estimates involve assumptions and judgment, introducing a level of uncertainty into the accuracy of the statements.
For example, the estimation of bad debt expense requires management to predict the amount of uncollectible accounts receivable. Similarly, depreciation expense involves estimating the useful life of long-term assets. Any inaccuracies in these estimates can significantly impact the financial statements.
Estimation errors can arise due to biases, inadequate information, or changes in market conditions. Moreover, different individuals within an organization may have varying opinions and judgments, leading to inconsistencies in financial reporting.
The reliance on estimates adds a layer of subjectivity to financial statements, making them more susceptible to manipulation or misrepresentation. Investors and stakeholders must be aware of the limitations and exercise caution when interpreting the figures.

In conclusion, the challenges in accuracy pose significant limitations to financial statements. Errors in data entry and the dependence on estimates can introduce inaccuracies and subjectivity into the reporting process. Understanding these limitations and implementing robust controls are crucial for maintaining the reliability and integrity of financial statements.
Limited Future Predictions
Financial statements primarily provide a historical perspective, making it challenging to foresee future market changes accurately.
Historical Perspective
Financial statements offer a historical view of a company’s financial performance. They reflect past revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities, providing essential insights into the company’s financial health.
Inability To Foresee Market Changes
Financial statements have limitations when it comes to predicting future market changes effectively. Since they are based on past data, they may not fully capture potential market shifts, consumer behavior changes, or industry disruptions.
Neglecting Intangible Assets
When it comes to financial statements, one of the limitations often overlooked is the neglect of intangible assets. While traditional financial reporting primarily focuses on tangible assets and liabilities, it fails to account for the value derived from intangible assets such as brand value and employee skills. This oversight can significantly impact the accuracy of financial statements and hinder a comprehensive understanding of a company’s true worth.
Omission Of Brand Value
The omission of brand value from financial statements can lead to a distorted representation of a company’s overall worth. Brands are valuable assets that can greatly influence consumer behavior and market positioning. However, due to accounting regulations, brand value is often excluded from balance sheets and income statements. As a result, investors and stakeholders may not fully grasp the true impact of a company’s brand on its financial performance, leading to potential misinterpretations.
Exclusion Of Employee Skills
Similarly, the exclusion of employee skills as intangible assets poses a limitation in financial reporting. While employee salaries are accounted for as expenses, the invaluable skills, knowledge, and experience that employees bring to a company are not reflected in financial statements. This oversight can obscure the true human capital value within an organization, affecting assessments of long-term sustainability and competitive advantage.
Ignoring Timing Issues
One limitation of financial statements lies in overlooking timing issues, which can lead to a distorted view of a company’s financial position. Ignoring the precise timing of transactions can impact the accuracy of the statements, potentially misleading stakeholders and investors.
Ignoring Timing Issues When it comes to financial statements, there are several limitations that need to be considered. One of these limitations is the ignoring of timing issues. This refers to the fact that financial statements are prepared based on historical data and do not account for the timing of certain transactions. Ignoring timing issues can lead to inaccurate financial statements and potentially misleading information for stakeholders. Recording Transactions Incorrectly When recording transactions, it is crucial to ensure accuracy and completeness. However, financial statements may be limited in their ability to capture transactions correctly. This can happen due to errors in recording, such as data entry mistakes or misunderstandings of accounting principles. These errors can lead to misrepresentation of the financial position of a company and affect decision-making processes. Recognition of Revenues and Expenses Another limitation of financial statements is the recognition of revenues and expenses. Financial statements may not accurately reflect the timing of when revenues are earned or when expenses are incurred. For instance, a company may provide services but not receive payment until a later date. In this case, the financial statements may not properly reflect the revenue earned in the period the services were provided. Similarly, expenses may be recognized before they are actually incurred or may be deferred to future periods. This can impact the profit or loss reported in a specific period and can distort the financial performance of a company. Table: Examples of Timing Issues in Financial Statements | Issue | Description | |————————-|————————————————————————————————–| | Revenue Recognition | Revenue recognition may not align with the period in which the goods or services are provided | | Expense Recognition | Expenses may be recognized before they are incurred or deferred to future periods | | Accruals and Deferrals | Accruals and deferrals can impact the timing of recognizing revenues and expenses | Unordered List: Impact of Ignoring Timing Issues – Inaccurate representation of financial position – Misleading information for stakeholders – distorted financial performance – Potential errors in decision-making processes In conclusion, the ignoring of timing issues is a significant limitation of financial statements. The recording of transactions incorrectly and the recognition of revenues and expenses not aligning with the timing can lead to inaccurate and potentially misleading information. It is essential for companies to be aware of these limitations and take appropriate measures to ensure the reliability and usefulness of their financial statements.Oversimplification Of Complex Transactions
Financial statements may oversimplify intricate contract terms affecting the true financial picture.
Complex financial instruments might not be fully represented accurately in statements.
Lack Of Non-financial Information
One of the limitations of financial statements is the Lack of Non-Financial Information. Non-financial data is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of a company’s performance.
Environmental Impact
Financial statements do not capture a company’s impact on the environment. Organizations nowadays are expected to be environmentally conscious and sustainable.
Employee Satisfaction
Employee satisfaction is often overlooked in financial statements. Happy employees are productive employees and directly contribute to a company’s success.
Regulatory Compliance Limitations
One of the major limitations of financial statements is the impact of regulatory compliance on their accuracy and usefulness. Regulatory requirements can impose certain constraints on how financial information is reported and disclosed, which can limit the effectiveness of financial statements in providing a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. In this article, we will explore two key regulatory compliance limitations that affect financial statements: Varying Accounting Standards and Legal Disclosure Constraints.
Varying Accounting Standards
The first limitation arises from the existence of varying accounting standards across different jurisdictions and regulatory bodies. Each country or region may have its own set of accounting principles and practices, making it difficult to compare financial statements of companies operating in different markets. This lack of harmonization can result in inconsistencies in the recognition, measurement, and presentation of financial information, leading to challenges in assessing the true financial position and performance of a company globally.
To address this limitation, efforts have been made towards convergence and the adoption of international accounting standards, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). However, full convergence is still a work in progress, and companies may have to comply with multiple reporting frameworks, further complicating the interpretation and analysis of financial statements.
Legal Disclosure Constraints
Another limitation stems from legal disclosure constraints imposed on companies, often for reasons of protecting sensitive information or ensuring fair and accurate representation. These constraints can restrict the extent to which companies can disclose certain financial details and non-financial information that may be relevant for stakeholders.
For example, companies may be prohibited from disclosing pending legal proceedings or sensitive business strategies. While these constraints aim to safeguard the company’s interests, they may hinder the ability of financial statements to provide a complete picture of the risks and opportunities facing the business. This limitation makes it important for users of financial statements to consider supplementary information from other sources, such as management discussions and analysis, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the company’s operations.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance limitations impact the accuracy and scope of financial statements. Varying accounting standards make it challenging to compare financial information across different jurisdictions, while legal disclosure constraints can restrict the amount and type of information disclosed. Understanding these limitations is crucial for users of financial statements to make well-informed decisions and to supplement their analysis with additional information as needed.
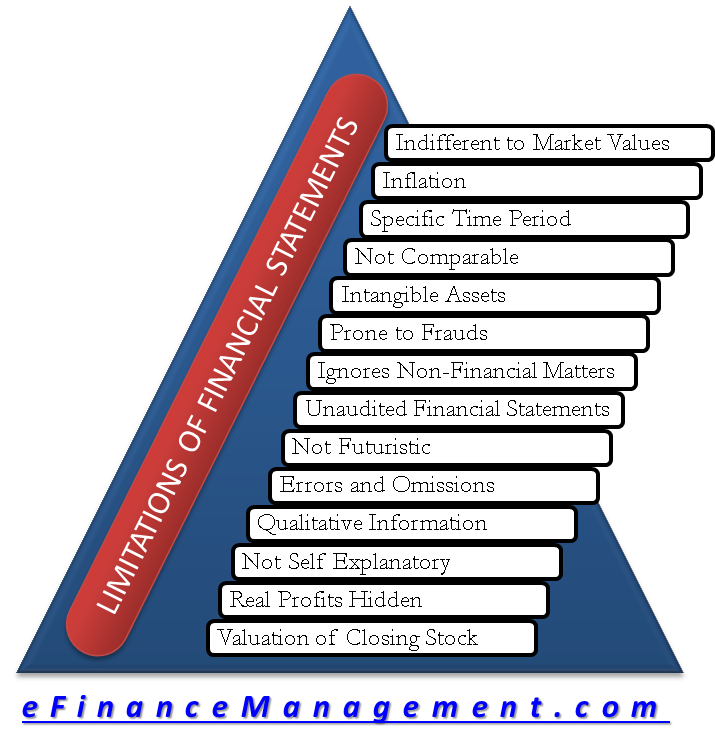
Credit: efinancemanagement.com

Credit: www.educba.com
Frequently Asked Questions For What Are The Limitations Of Financial Statements
What Are The Five Limitations Of Financial Statements?
The five limitations of financial statements are: 1. Historical information only 2. Not adjusted for inflation 3. Can be manipulated 4. Doesn’t reflect market value 5. May not include qualitative factors.
What Are The 4 Limitations Of Financial Accounting?
The limitations of financial accounting are: 1. It focuses on historical data, not future predictions. 2. It can be manipulated to present a favorable picture. 3. It doesn’t capture non-financial information that impacts decision-making. 4. It doesn’t account for the value of intangible assets like employee satisfaction.
What Are The 5 Limitations Of The Income Statement?
The 5 limitations of the income statement are: inability to show non-financial data, not considering the time value of money, not reflecting changes in asset values, not accounting for inflation, and not fully capturing all expenses.
What Are The Limitations Of Notes To Financial Statements?
Limitations of notes to financial statements include complexity, potential oversight risks, overwhelming detail, and varying disclosure standards.
What Are The Key Limitations Of Financial Statements?
Financial statements may not reflect true financial health due to estimation errors and omitted items.
Conclusion
To sum up, financial statements provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and position. However, it is essential to recognize their limitations. These include the reliance on historical data, the omission of non-financial information, and the subjectivity of certain accounting principles.
By acknowledging these limitations, decision-makers can supplement financial statements with other information sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s true financial health. Ultimately, using a combination of financial statements and additional analysis tools ensures a more holistic assessment and informed decision-making process.



