Financial database entities encompass vital features such as data security, scalability, flexibility, and integration capability. These features enable efficient storage, retrieval, and management of financial data.
In the digital age, financial database entities play a crucial role in the management of financial information, providing secure storage, accessibility, and reliable data processing. With features like data security, scalability, flexibility, and integration capability, these entities offer robust solutions for managing complex financial information.
We will delve into the main features of financial database entities, highlighting how these capabilities contribute to optimizing financial data management and decision-making processes within organizations. Understanding the importance of these features is paramount for businesses and financial institutions aiming to streamline their operations and enhance data security and integrity.
Structure Of Financial Database Entities
A financial database is a collection of structured data that is designed specifically for storing and managing financial information. It plays a crucial role in organizing and processing financial data efficiently. Understanding the structure of financial database entities is essential to seamlessly navigate and utilize the data within.
Data Tables
Data tables are fundamental components of financial database entities. They are used to organize and store vast amounts of financial information in a structured manner. Each table represents a specific category of data, such as customers, transactions, or assets. For example, a customer table may contain columns for customer ID, name, address, and contact details.
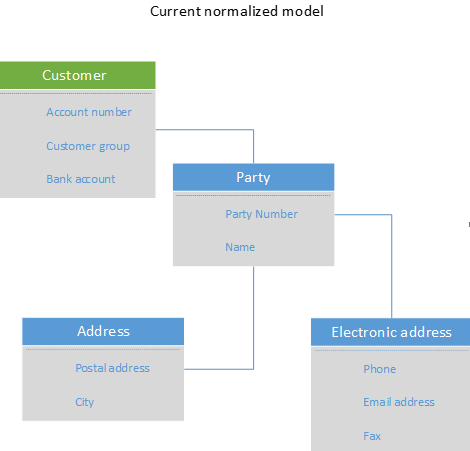
Relationships Between Entities
In a financial database, various entities are interconnected through relationships, which allow for the retrieval and analysis of complex financial information. These relationships establish connections and dependencies between different data tables. For example, a transaction table may have a foreign key that links it to the customer table, indicating which customer made the transaction.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/spv-Final-974453786ede4673a9c980206543bfad.jpg)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Key Components
Key Components: Financial database entities have key components that are vital for their functionality. Understanding these components is crucial for managing financial data efficiently.
Attributes
Attributes are the characteristics or properties of a financial database entity. They represent the data that the entity will contain. Each attribute holds specific information, such as customer name, account number, transaction date, and so on. These attributes are essential for organizing and retrieving data effectively.
Primary Keys
Primary keys are unique identifiers for each record within a financial database entity. They ensure that each record is distinct and can be accessed without ambiguity. Having a primary key is crucial for maintaining data integrity and enabling efficient retrieval of specific records.
Foreign Keys
Foreign keys establish relationships between different entities within a financial database. They link the primary key of one entity to the foreign key of another, facilitating the normalization of the database and ensuring data consistency. Utilizing foreign keys accurately is vital for maintaining the integrity and coherence of financial data.
Data Modeling In Financial Databases
In the realm of financial databases, data modeling is an essential component that aids in organizing and structuring financial data in a way that facilitates effective management and analysis. It involves creating a blueprint of the database by utilizing various techniques such as Entity-Relationship Diagrams and Normalization. Let’s delve into these main features of financial database entities and understand how they contribute to the robustness and efficiency of financial databases.
Entity-relationship Diagrams
Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) serve as visual representations of the entities within a database and the relationships between them. In the context of financial databases, ERDs allow for a clear depiction of the various financial elements such as accounts, transactions, and entities, along with their interconnections. They are instrumental in illustrating the logical structure of the financial database, providing a visual roadmap for understanding the relationships and dependencies between different financial entities.
Normalization Techniques
Normalization is a vital process in data modeling that aims to minimize redundancy and dependency within a database, thereby enhancing its efficiency and integrity. In financial databases, normalization techniques like First Normal Form (1NF), Second Normal Form (2NF), and Third Normal Form (3NF) play a crucial role in organizing financial data into logically structured tables. By eliminating data redundancy and minimizing anomalies, normalization ensures that the financial database is optimized for storage, retrieval, and analysis, contributing to accurate financial reporting and analysis.
Security Measures
Financial database entities employ robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information. These measures include encryption protocols, multifactor authentication, regular backups, and strict access controls to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. With these main features, financial databases provide a secure environment for storing and managing financial data.
Introductory Paragraph:
Security measures play a crucial role in financial database entities to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Financial institutions and businesses dealing with financial data need robust security systems to safeguard their databases from potential threats. Incorporating access control and encryption are primary features that are essential for maintaining data security.
Access Control:
Access control is a fundamental security measure implemented in financial database entities. It involves setting up restrictions and granting access privileges to authorized personnel only. By enforcing access control mechanisms, financial institutions can ensure that only authenticated individuals with proper credentials can access confidential financial data. Access control may include user authentication, role-based access control, and granular permission settings.
Encryption:
Encryption is another critical security feature in financial database entities, ensuring that sensitive data remains unreadable and protected from unauthorized access. By converting data into an encrypted format using advanced algorithms, even if an unauthorized individual gains access to the data, they will be incapable of deciphering its meaning. Encryption prevents data breaches by providing an extra layer of security, making it significantly more challenging for cybercriminals to steal confidential financial information.
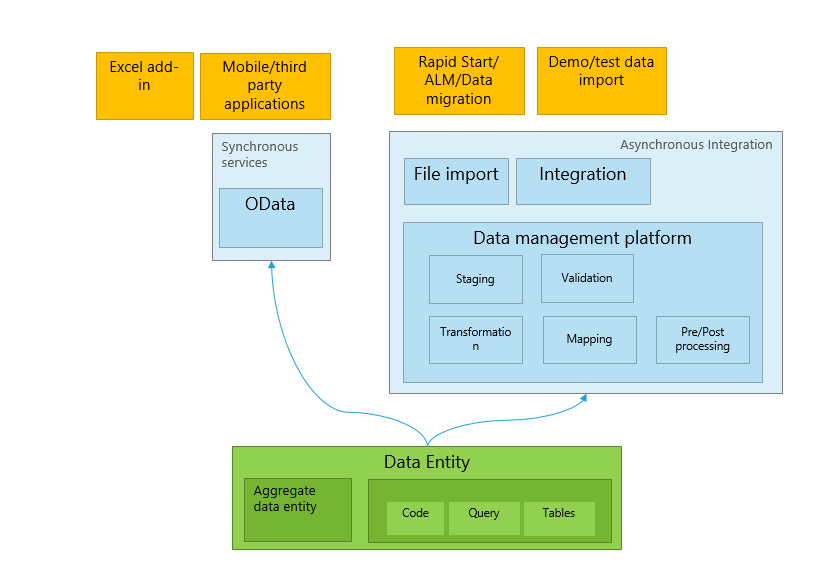
Integration With Financial Systems
Erp Systems
ERP systems are integral for managing a company’s resources efficiently.
Crm Systems
CRM systems play a crucial role in maintaining customer relationships.
Credit: learn.microsoft.com
Challenges And Future Trends
Challenges and Future Trends:
The financial industry is rapidly evolving, presenting a host of challenges and future trends that financial database entities must navigate. From big data handling to blockchain integration and compliance regulations, staying ahead of the curve is crucial.
Big Data Handling
Financial database entities face the challenge of managing large volumes of data. Efficient processes for big data handling are essential for analysis and decision-making.
Blockchain Integration
Integrating blockchain technology can enhance security and transparency for financial transactions. Blockchain integration offers decentralized solutions.
Compliance Regulations
Adhering to ever-changing compliance regulations is critical for financial database entities. Staying compliant ensures trust and credibility in the industry.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/financialstatements-final-d1268249b5284b3989c979ee82f2869e.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Frequently Asked Questions For What Are The Main Features Of Financial Database Entities
What Are Financial Database Entities?
Financial database entities are structures that store and organize financial information for analysis and reporting. They include tables, rows, and columns for data storage. These entities help in data retrieval, manipulation, and presentation for financial decision-making.
What Are The Entities Of A Database?
Entities of a database include tables, which store structured data, and relationships that connect tables. Each table represents a specific type of data. Understanding entities is crucial for organizing and managing data effectively.
What Are The Types Of Data In Finance?
There are several types of data in finance, including market data, earnings data, financial performance data, and macroeconomic data. These data sets help analysts and investors make informed decisions and evaluate the financial health of companies and economies.
What Type Of Data Are Financial Details?
Financial details are classified as sensitive personal information. They include bank account numbers, credit card information, and income figures.
What Are The Key Features Of Financial Database Entities?
Financial database entities include secure data storage, real-time updates, audit trails, robust reporting, and scalability.
Conclusion
Financial database entities play a crucial role in managing and organizing financial information. With their main features like data storage, retrieval, and analysis, these entities enable businesses to make informed decisions and ensure regulatory compliance. By leveraging the power of financial databases, organizations can streamline their operations, enhance data accuracy, and improve overall financial performance.
Embracing these key features is essential for staying ahead in the dynamic world of finance. So, make the most of financial database entities to optimize your financial processes and drive growth.